TL; DR: Three Wide-Spread Stakeholder Failures
There are plenty of Scrum stakeholder failures. Given that Scrum is a framework with a precise and concise yet short “manual,” this effect should not surprise anyone. While the Scrum Guide makes numerous references to stakeholders in Scrum, stakeholders themselves are no official role (accountability), no matter their crucial contribution to a Scrum team’s overall success.
Explore with me three widespread examples of how stakeholders fail their Scrum teams in three short video clips, totaling 6 minutes and 5 seconds.
🗞 Shall I notify you about articles like this one? Awesome! You can sign up here for the ‘Food for Agile Thought’ newsletter and join 31,000-plus other subscribers.
🎓 Join Stefan in one of his upcoming Professional Scrum training classes!
Join more than 210 peers from May 27-29, 2021, for the Virtual Agile Camp Berlin 2021, a live virtual Barcamp using open space technology principles and practices.
The Scrum Guide on Stakeholders
Let’s refresh our memories regarding stakeholders according to the 2020 Scrum Guide. While stakeholders are not an official accountability, the Scrum Guide makes numerous references to stakeholders in Scrum:
- Page 4: The Scrum Team and its stakeholders are open about the work and the challenges.
- Page 5: The Scrum Team is responsible for all product-related activities from stakeholder collaboration, verification, maintenance, operation, experimentation, research and development, and anything else that might be required.
- Page 6: The Product Owner is one person, not a committee.
- Page 6: The Product Owner may represent the needs of many stakeholders in the Product Backlog.
- Page 6: Those wanting to change the Product Backlog can do so by trying to convince the Product Owner.
- Page 7: The Scrum Master serves the Product Owner in several ways, including facilitating stakeholder collaboration as requested or needed.
- Page 7: The Scrum Master serves the organization in several ways, including helping employees and stakeholders understand and enact an empirical approach for complex work.
- Page 7: The Scrum Master serves the organization in several ways, including removing barriers between stakeholders and Scrum Teams.
- Page 8: The Scrum Team may also invite other people to attend Sprint Planning to provide advice.
- Page 8: [Sprint Planning: Why is this Sprint valuable?] The whole Scrum Team then collaborates to define a Sprint Goal that communicates why the Sprint is valuable to stakeholders.
- Page 9: The Scrum Team presents the results of their work to key stakeholders and progress toward the Product Goal is discussed.
- Page 9: During the event, the Scrum Team and stakeholders review what was accomplished in the Sprint and what has changed in their environment. Based on this information, attendees collaborate on what to do next.
- Page 10: The Scrum Team inspects how the last Sprint went with regards to individuals, interactions, processes, tools, and their Definition of Done.
- Page 10: These [Artifact] commitments exist to reinforce empiricism and the Scrum values for the Scrum Team and their stakeholders.
- Page 12: However, an Increment may be delivered to stakeholders prior to the end of the Sprint.
- Page 12: The Definition of Done creates transparency by providing everyone a shared understanding of what work was completed as part of the Increment.
Source: The Scrum Guide on stakeholders. (This aggregation is from the Scrum Guide 2020 Reordered.)
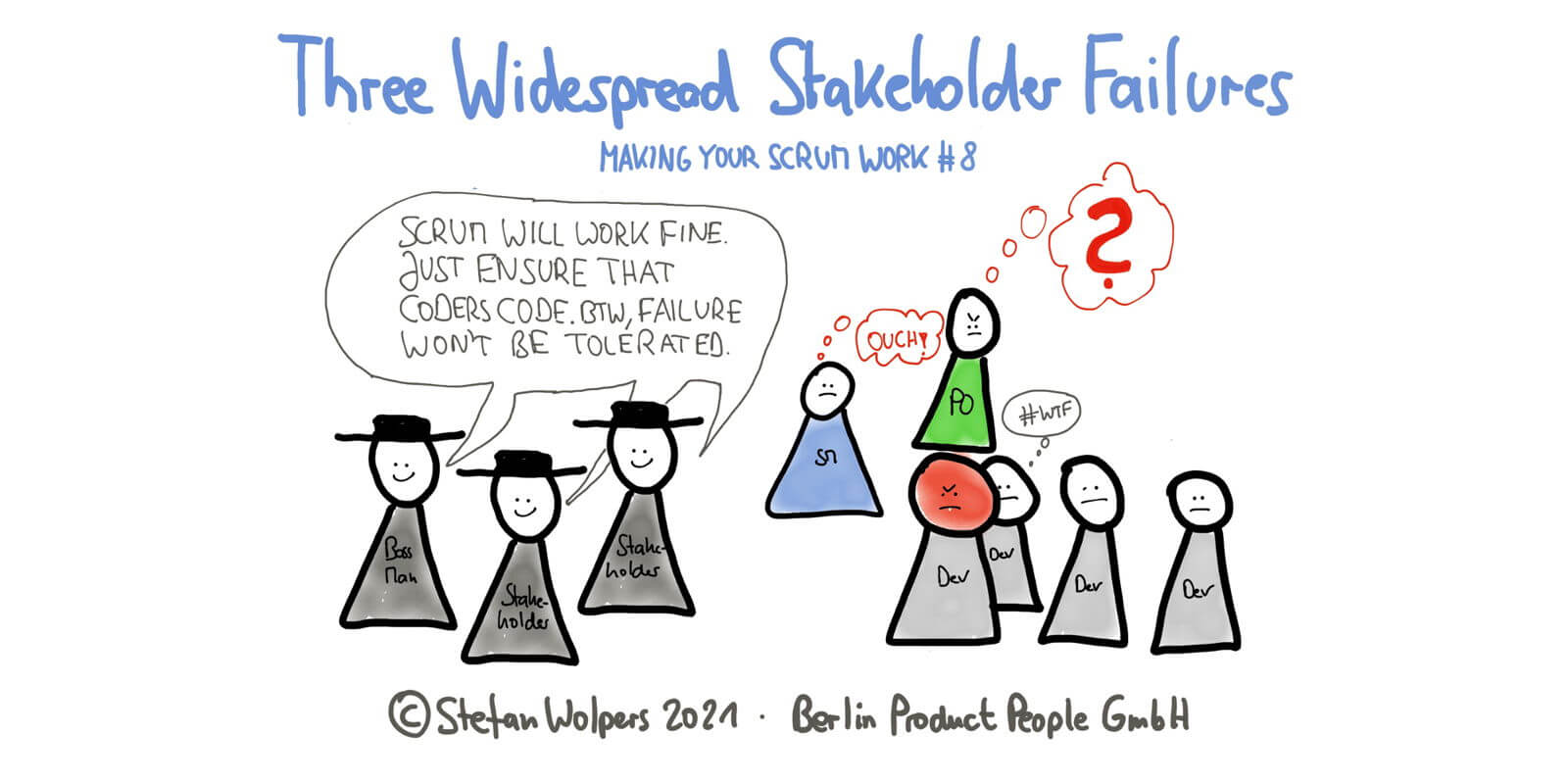
Three Wide-Spread Stakeholder Failures
Let me point at three Scrum stakeholder failures that have the potential to derail your organization’s attempt at achieving business agility with Scrum:
Turning the Sprint Review into a Stakeholder Approval Instance
In my experience, the Sprint Review acceptance gate by stakeholders is an anti-pattern typical for organizations that are still rooted in the industrial paradigm, exercising command & control. Some of the reasons for this anti-pattern are:
- A “my budget, my feature” attitude on the stakeholder side. The Scrum Team is seen as an internal agency, delivering requirements issued by the stakeholders.
- The organization probably follows a metered funding approach, for example, providing a budget for the Scrum Team’s development effort only for a short period.
- There is a general lack of trust in a Scrum Team’s ability to manage itself successfully.
- Middle managers might even fear becoming obsolete after a successful agile transformation and try to stay their ground.
Generally, this example among stakeholder failures is a sign for an agile transformation that is not fully supported by all stakeholders.
Coders Code; They Don’t Talk to Customers
Adhering to the inherited functional silos, Developers are supposed to deliver “code” and only code. They are not supposed to talk to customers or take over customer support duties to understand their problems first-hand.
From my perspective, that is pure Taylorism at work, entirely output-oriented. The problem is, we are no longer assembling Model-Ts. But we go every day, where no one has ever gone before. In a complex environment, those closest to a problem are best suited to make the right decision to solve it.
Hence, it becomes necessary that all Scrum team members talk directly with customers to understand their challenges better and avoid the misallocation of the Scrum team’s development time. (My rule of thumb: Coding is no more than 50 % of the whole effort of creating value for our customers. The best way to increase the productivity of a Scrum team is to avoid building unnecessary stuff. Now, guess how you can best address this issue? Right: Developers talk to customers.)
There Is no Failure Culture
A former client of mine, a large utility company, practiced at the time a no-failure approach to promotions: A failed project on your internal record meant you would not take the next step on the career ladder. As a result, everyone played safe, which resulted in short-term orientation as not-failing became more important than innovation. Consequently, the organization was increasingly struggling to attract new (tech) talent when software started eating the world.
Suppose “good” failure is not celebrated as a critical part of the learning process, and incrementalism becomes the name of the game. In that case, the Innovator’s Dilemma, as coined by Clayton Christensen, becomes a more likely fate of the organization. When resilience is a worthwhile goal to achieve, think of Netflix’s chaos monkey, failure needs to be an option.
And failure needs to be openly discussed—without repercussions—so everyone can learn from the case. And as it should be, leaders need to confess first. One approach could “failure nights,” or sharing your wrong decisions from the past openly. For example, see Bessemer Venture Partners’ “The Anti-Portfolio. Honoring the companies we missed.”
The Conclusion: Three Wide-Spread Stakeholder Failures
While the Scrum Guide is not honoring the crucial contribution of stakeholders for the Scrum team’s success formally, it does acknowledge their importance on numerous occasions. Interestingly, despite the severe consequences of stakeholders failing their Scrum teams, stakeholders are often not a prime focus of Scrum Masters. (Probably, because the organization is reserving the job to “agile coaches?” That would be just another anti-patterns at the organizational level.)
As a result of this neglect, these stakeholder failures may create teams of mercenaries that trade time to collect a paycheque at the end of the month, which paves the path to mediocrity, not to business agility. (After all, Scrum is a team sport, and no one is benching.)
What Scrum stakeholder anti-patterns have you observed? Please share them with us in the comments.
📖 Stakeholder Failures — Related Posts
32 Scrum Stakeholder Anti-Patterns
Three Wide-Spread Scrum Master Failures in 5:31 Minutes—Making Your Scrum Work
27 Sprint Anti-Patterns Holding Back Scrum Teams
A Sprint Review without Stakeholders — Making Your Scrum Work #3
📅 Scrum Training Classes, Workshops, and Events
You can secure your seat for Scrum training classes, workshops, and meetups directly by following the corresponding link in the table below:
See all upcoming classes here.
You can book your seat for the training directly by following the corresponding links to the ticket shop. If the procurement process of your organization requires a different purchasing process, please contact Berlin Product People GmbH directly.
✋ Do Not Miss Out and Learn about Stakeholder Anti-Patterns: Join the 12,000-plus Strong ‘Hands-on Agile’ Slack Team
I invite you to join the “Hands-on Agile” Slack team and enjoy the benefits of a fast-growing, vibrant community of agile practitioners from around the world.
If you like to join now all you have to do now is provide your credentials via this Google form, and I will sign you up. By the way, it’s free.





I do not have an experience with the environment you mentioned. But I do have some questions. (1) Command and control based companies, I presume, are concerned about maintaining status quo and are prone to maintain least risk acceptance levels. Would such a mindset look for innovation too? (2) Teams that are really innovative by nature… would they not be innovative regardless of the leadership style
Stakeholder Failure. Presence of a stakeholder who is well deep rooted in pre-historic project management methodology, carries an averse to Agile, looking for every opportunity to derail this project and is a member of Sprint Review team. Additionally, the Scrum Team fail to spot this negative contributor until late in the project when enough damage is already done
In my experience there is a direct correlation between companies that want to HAVE innovation and ones that have command and control approaches to allowing failure and the leadership style. Leaders who demand control can’t fathom why there is no innovation on the team. Teams become so risk adverse that only the simplest changes get made. These changes then grow in point size so even something simple is sized as complex.