TL;DR: On the Benefits of Offline Boards
Offline boards lift a team’s level of collaboration significantly. They are great information radiators for stakeholders, and they massively benefit from the psychology of getting haptic. Learn the best practices of getting started with your own offline boards in this third post of our series on how to kick-off an agile transition.
Note: see the latest version of the board below.
🗞 Shall I notify you about articles like this one? Awesome! You can sign up here for the ‘Food for Agile Thought’ newsletter and join 30,000-plus other subscribers.
Join more than 120 peers from May 27-29, 2021, for the Virtual Agile Camp Berlin 2021, a live virtual Barcamp using open space technology principles and practices.
On the Benefits of Offline Boards
“When you put problem in a computer, box hide answer. Problem must be visible!” (Hideshi Yokoi, former president of the Toyota Production System Support Center in Erlanger, Kentucky, USA)
Mr. Yokoi’s insight points directly at the heart of the problem: Tools like Jira look tempting to handle the administrative side of agile projects. However, utilizing these tools quickly turns into a slippery slope as they inherently favor the creation of “busy work” over valuable work on the product.
These tools tend to reduce transparency for the sake of administrating issues and tasks. Some team members thus may be less motivated to accept their part of the team’s accountability to get things done—bookkeeping does not ship valuable product increments.
The solution is simple: Have an offline – or physical – board at the heart of your team’s project, and don’t rely solely on software solutions. The positive (psychological) effects of writing or sketching on a piece of paper, touching, and moving it cannot be overestimated.
Download the ‘Agile Transition – A Manual from the Trenches’ Ebook
The “Agile Transition – A Hands-on Guide from the Trenches” ebook is a collection of articles I have been writing since October 2015. They detail the necessary steps to transition an existing product delivery organization of over 40 people to agile practices. Download it for free:
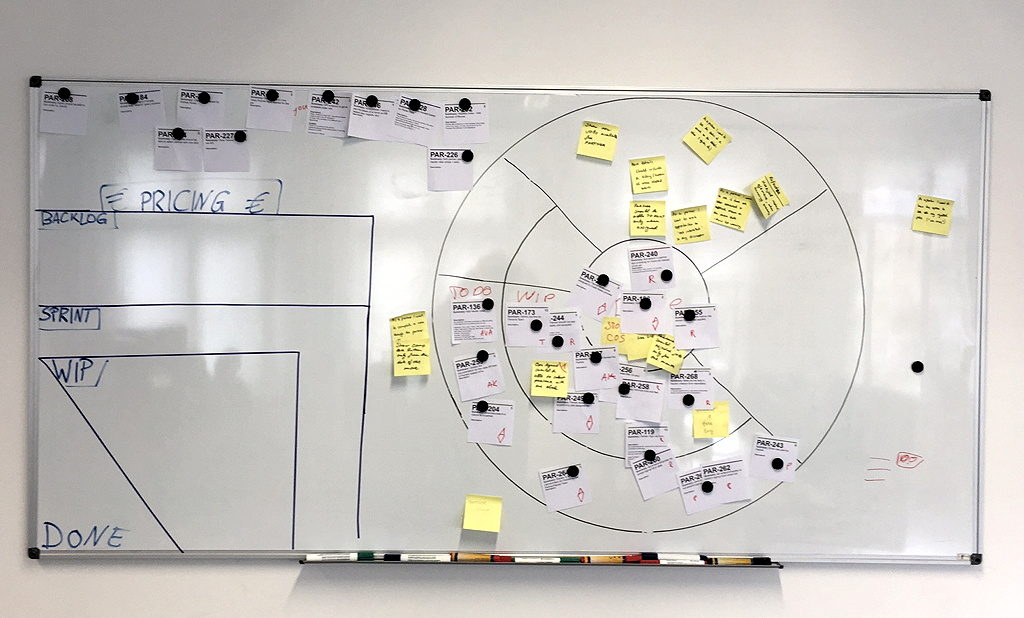
Components of an Offline Board
Offline boards vary from team to team, effected by the culture of the organization, the maturity of the product, team size, policies, and various other factors. There are, however, some basic components that are beneficial for all teams:
- Display all policies affecting the work, e.g. both the “Definition of Ready” and “Definition of Done”, or the working agreement.
- Have a schedule with all ceremonies: When is the team gathering for stand-ups, product backlog refinements and sprint planning sessions, sprint reviews, and the team retrospective?
- Provide all information on the sprint, including the sprint goal.
- Organize the sprint backlog: All issues in the backlog are prioritized. (Choose your style: From top to bottom, or from left to right—as long as it is systematic, and works for the team, you cannot be wrong.)
- Create issue lanes: Only one issue per lane. (Tip: Limit the space of the lanes to the size of your index cards or Post-it stickies.)
- Set up all workflow stages depending on the team’s workflow.
- Consider adding an express lane for issues that require the immediate attention of the team without having been picked for the current sprint. (Tip: Don’t set up an express lane without a strict code defining access to it. Otherwise, stakeholders will be tempted to push for all issues becoming “express lane eligible”.)
- List the do-not-disturb hours.
- Show an availability chart: Who is available during the current sprint?
- Finally, add some board art: Why not start with the team logo?
Office Supplies for Offline boards
The basic office supplies (and other materials) that you will need besides a whiteboard and a variety of markers are:
- Have magnetic avatars of all team members made: They are both fun and highly effective to visualize who is working on what issues at any given moment. (In Germany, I source the magnetic avatars from magpics; they are less than a one Euro per piece.)
- You will need tape, 3mm wide. (You don’t want to separate lanes on a whiteboard with normal markers, as they need to be redrawn all the time, and tend to soil clothes.)
- Use Post-its in various colors to support color-coding. (Tip: Spend extra on the “Super sticky” version, as normal Post-its will fall off boards too quickly.)
- Alternatively, use colored index cards.
- Buy small magnets as even super sticky Post-its fall off when it’s hot or humid, for example.
- Provide a sharpie to dot tasks or issues that are taking longer than a working day.
- Consider sourcing colored paper to print issues or tasks, and color code them if no color printer is available.
Best practices
The following practices have proven to be successful over the years. If your team is new to offline boards, don’t start with all of them at once that would a) be overwhelming, and b) limit the team’s interest in experimenting with the board design to figure out what is working for them. Remember: It is not your board, but the team’s:
- Building the board is a team exercise, not the Scrum master’s obligation: Setting the board up in the first place, as well as maintaining it over the sprints. (And each has team will have its own taste.)
- Color-coding the issues massively improves the user experience of the board: User stories, bugs, technical tasks, spikes. Don’t forget to provide a legend that explains the color code to the observer.
- Have your standups in front of the board.
- If you are using in JIRA®, invest in Agile Cards.
- Use tasks to break down issues into smaller work items. There are several reasons for doing that:
- Tasks easily visualize progress, if they are moved individually through the stages until the issue itself is “done”.
- Create small tasks: Each task shouldn’t take longer than a day. If that span is exceeded, it might indicate an impediment or the issue itself is not as well understood as previously thought.
- If the team members initial each task, it becomes immediately transparent who is working on what. (Alternatively, you also can use magnetic avatars to achieve this as well.)
- Some teams like to create tasks utilizing the online ticket system, e.g. Jira. Other teams create handwritten stickies during sprint planning II. Both approaches are working well.
- Move tasks through the workflow stages during the standups, unless your team’s tasks are so small that each team member accomplishes several of those during a day. In this case, updating the board independently of the standups will better visualize the state of the sprint at any given moment.
- Mark all tasks that are taking more than one day to accomplish by adding a new dot every day to identify potential blockers, process or organizational problems. (Note: This practice is not meant to track a team member’s productivity.)
- Limit work in progress: To get things done, it does not help to start working on a new issue when the one you were previously working on is blocked. Hence, limit the number of tasks the team can work on in any workflow stage:
- You could simply display the “WIP” limit above each category.
- On top of that, you can use a grid structure: “Enforcing” the work in progress limit by limiting the available space for stickies.
- Alternatively, if your team is using magnetic avatars, you can just limit the number of avatars available per team member instead, e.g. to three or four.
- By the way, offline boards work for distributed teams, too. Just use a camera during the standups to update the remote team members, and move their issues on their behalf.
- Last, but not least: Experiment. Boards—beloved by their teams—usually go through several iterations before the team settles on a design.
Update 2016-10-23:
An ugly duckling turned swan: the final version of the offline board from above. The first draft proved to be a good design for the team. We are still waiting for colored magnetic sheets to replace the stickies, though.
I particularly like the small board game the team integrated. It’s fun to play with the little neodymium magnets…
Conclusion
Offline boards improve a team’s understanding of the situation of a sprint at any given time and thus lift the collaboration among team members to a higher level. They are great information radiators for stakeholders and benefit from the psychology of getting haptic.
As a Scrum master, you should remember, though: It is not your board, it is the team’s board. Experiment!
Related Posts
How to Kick-off Your Agile Transition (Part 1)
Product Backlog Refinement — Agile Transition Part 2
10 Proven Stakeholder Communication Tactics during an Agile Transition
📅 Scrum Training & Event Schedule
You can secure your seat for Scrum training classes, workshops, and meetups directly by following the corresponding link in the table below:
See all upcoming classes here.
You can book your seat for the training directly by following the corresponding links to the ticket shop. If the procurement process of your organization requires a different purchasing process, please contact Berlin Product People GmbH directly.







Valid point, John. Thanks a lot for your comment!
I’m a business change and program management consultant and I’ve been turning teams and organisations agile for the past 10 years. I want to start of by saying that your mail and blog is by far my favourite – please keep up the good work.
What brought me to writing the reply is your comment at the end of the article “offline boards work for distributed teams, too. Just use a camera during the standups to update the remote team members, and move their issues on their behalf.” I feel you are trying too hard to find a ‘fit’ for physical boards across all agile team structures.
Physical boards are excellent for co-located teams that work on small project increments and who have control of the end-to-end of their delivery (the classic single scrum team model). In my opinion, once you go outside these ideal team types then digital collaboration is a must.
A small team without co-located members needs to be more digital, not less – they need collaborative workspaces, integrated tool sets (I love Swagger) integrated build and release notes. No matter how much office space you have anyone looking at post-its that are moved by a third party will definitely have less connection to ‘their work’ than someone who drags the digital card to the next stage. I typically run a Webex/Video Chat for this kind of team and enforce the scrum discipline on the phone.
When I have more than one pod working on a project and the pod is remote I encourage each pod to create create their own boards and at the scrum of scrums we track to the definition of done using dependency stories. This allows teams to work Kanban, scrum or even waterfall but meet on the same physical board. However, these physical boards should be used as a focal point locally (as you say) but integrating these efforts is always much safer and easier to manage using a tool. This is especially true if deliveries need to be integrated.
Thanks you again for your great work and blog – you’re doing a great job.
Good point, Michael, it’s comfortable in the shadow… 🙂
Could not agree more. I’ve found that teams the do not want to use physical boards do not really want to be transparent.